
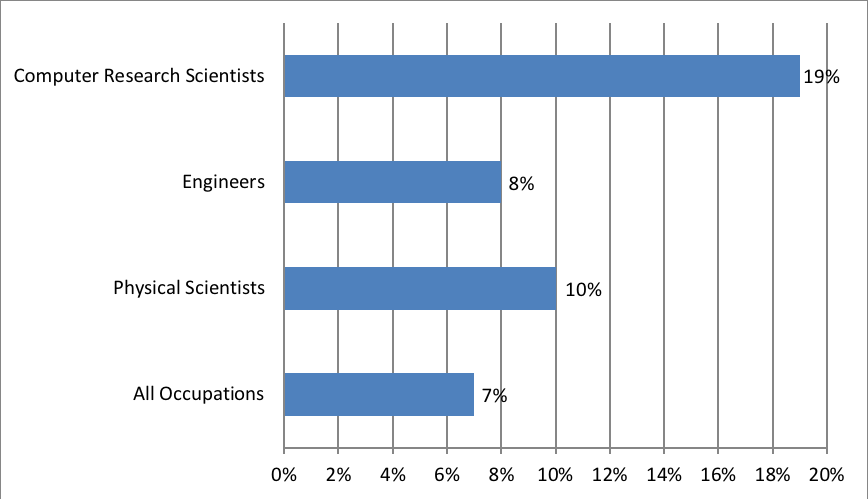
This article is for you if you're interested in a biochemical income. This article will discuss biochemical salaries in BOTHELL (WA) and San Mateo (CA). To get started on your career, explore the different biochemical salary options. Find out more about the requirements for salary and job descriptions at Worthington Biochemical as well as Youtell Biochemical. Both companies have BOTHELL, WA headquarters and offer competitive benefits.
Youtell Biochemical salaries are $29 an hour
The average salary at Youtell Biochemical is $99,854. Salaries range from $88,159 up to $114,509. Salary ranges from $88,159 up to $114,509, depending on what the position is, how much education they have and the skills required. Below are examples of the jobs and salaries available at Youtell Biochemical. Also, the salary ranges depend on education and previous experience.
Youtell Biochemical has its headquarters in BOTHELL WA
Youtell Biochemical is an enzyme product-focused chemical company with headquarters in BOTHELL. They have a state-of-the-art biotechnology research center in Bothell, and two downstream processing and fermentation factories in China. Those companies use patented technologies to produce enzyme products. Youtell Biochemical can produce over 80,000 tons annually of enzyme products on their main campus in BOTHELL WA.
Worthington Biochemical is located in San Mateo (CA).
Worthington Biochemical was established in 1947. Charles Worthington was a Rockefeller Institute research assistant who had prepared crystalline enzymes for biochemical research. He realized quickly that reliable and high-purity enzymes were crucial for the biochemical research community. It would be difficult to purify them by researchers. Worthington started his own company in 1947, in Freehold, New Jersey, to supply these enzymes.
Worthington bought Cooper's Clinical Division in 1985. This was a biotech company based in New Jersey. This move allowed Worthington to expand its operations, while allowing it to focus more on the lucrative clinical market. The company was unable to expand into the molecular science and immunology fields. Instead, the company expanded its facility to formulate diagnostic kits, while devoting less resources to enzyme production.
FAQ
What is the job of a logistics manger?
A logistics manager ensures that all goods are delivered on time and without damage. This is done through his/her expertise and knowledge about the company's product range. He/she should also ensure enough stock is available to meet demand.
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
Can some manufacturing processes be automated?
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians invented the wheel thousands of years ago. We now use robots to help us with assembly lines.
There are many uses of robotics today in manufacturing. They include:
-
Automation line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Automation could also be used to improve manufacturing. For instance, 3D printing allows us make custom products and not have to wait for months or even weeks to get them made.
What are manufacturing & logistics?
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics covers all aspects involved in managing supply chains, including procurement and production planning. As a broad term, manufacturing and logistics often refer to both the creation and delivery of products.
How does a production planner differ from a project manager?
The major difference between a Production Planner and a Project Manager is that a Project Manager is often the person responsible for organizing and planning the entire project. While a Production Planner is involved mainly in the planning stage,
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
Production planners make sure that every aspect of the project is delivered on-time, within budget, and within schedule. They also ensure the quality of the product and service meets the client's requirements.
What skills is required for a production planner?
Production planners must be flexible, organized, and able handle multiple tasks. Also, you must be able and willing to communicate with clients and coworkers.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was developed by Taiichi Okono in Japan, during the 1970s & 1980s. TPS founder Kanji Takoda awarded him the Toyota Production System Award (TPS). Michael L. Watkins published the book "The Machine That Changed the World", which was the first to be published about lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean manufacturing has been deemed one of the best ways to manage the entire value-chain, including customers, distributors as well retailers and employees. Lean manufacturing is widely used in many industries. For example, Toyota's philosophy underpins its success in automobiles, electronics, appliances, healthcare, chemical engineering, aerospace, paper, food, etc.
Five basic principles of Lean Manufacturing are included in lean manufacturing
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce Waste – Eliminate all activities that don't add value throughout the supply chain.
-
Create Flow - Ensure work moves smoothly through the process without interruption.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing, although not new, has seen renewed interest in the economic sector since 2008. To increase their competitiveness, many businesses have turned to lean manufacturing. In fact, some economists believe that lean manufacturing will be an important factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
Lean manufacturing can be applied to almost every aspect of an organization. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three main types:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This method reduces lead times, increases availability, and decreases inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement involves continuous improvement of processes and people as well as tools.