
The Defense Industrial Base (DIB), a network of over 200,000 companies that provide goods and services for the Department of Defense, is more than 200,000. It includes startups, big corporations, small businesses. A new report by the Government Accountability Office outlines the risks the DIB faces and the challenges it faces in addressing them.
The defense industrial sector has suffered a nearly 40 percent decline over the past decade. This has made it difficult for the Department of Defense to attract new businesses into the sector. To address this issue, the Defense Department has tried a variety of efforts to encourage new businesses to participate. Despite these attempts, many smaller firms are being left behind. This has created a growing national security risk.
Many DOD agencies are currently working to mitigate risk in the DIB. However, the department has not developed a comprehensive strategy to assess and manage these risks. GAO conducted an analysis of several department reports and interviewed DOD representatives to determine where improvements could be made. GAO identified five elements which could help the department reach its goals.

Loss of commercial suppliers is one of the greatest concerns. Many of these companies supply parts for weapons systems used by the Pentagon. The number of small businesses in the industry has dwindled over the past decade, and there are not clear metrics on how many new companies are entering the market.
Other problems include material shortages as well as reliance on foreign vendors. Additionally, the military's acquisition process is often slowed by intellectual property restrictions, and there is no standard definition for what is considered a "new entrant" into the defense industrial base.
GAO recommended to the Department of Defense that it update its policy for mitigating risks in DIB. It is important that the department continues to engage traditional defense contractors, and develop tools that will allow commercial technology providers to gain access to the DoD marketplace. These suggestions should be part the overall strategy to address issues related to the industrial base.
As part of this strategy, it is important for the Defense Department to consider how its OTAs/CSOs can be used in order to expedite acquisition strategies development. If the right people, processes, technologies and technology are used, the supply chain can change to provide dynamic outcomes.
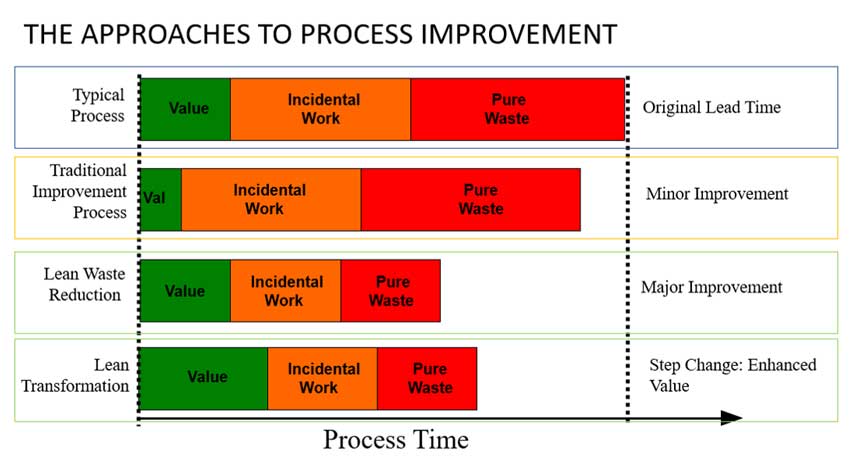
Despite a decrease in new entrants to defense industry base over the last decade the industry is still developing. For example, many companies are not comfortable with the traditional Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) process. Small businesses may have fewer options to compete in the current environment.
Innovation is key for the defense industrial sector. Small businesses and startups play a crucial role. The resilient DIB allows companies to support National Security while also allowing the Department of Defense better develop military equipment.
Overall, the defense industry base is a complex business that requires a comprehensive strategy. This strategy must ensure that resources are aligned to the needs of the military. In the meantime, it is essential that the Department of Defense learn more about best practices for integrating technology into its business processes, which will allow for more efficient and innovative products and services.
FAQ
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
Production planners ensure all aspects of the project are delivered within time and budget. They make sure that the product and services meet client expectations.
What skills do production planners need?
Being a production planner is not easy. You need to be organized and flexible. It is also important to be able communicate with colleagues and clients.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym 7R's of Logistic is an acronym that stands for seven fundamental principles of logistics management. It was created by the International Association of Business Logisticians and published in 2004 under its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The acronym is made up of the following letters:
-
Responsive - ensure all actions are legal and not harmful to others.
-
Reliable – have faith in your ability and capability to keep promises.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - Consider all aspects of operations, including environmental impact and cost effectiveness.
-
Respectful - Treat people fairly and equitably
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable provides value-added products and services to customers
What type of jobs is there in logistics
There are many types of jobs in logistics. Some of them are:
-
Warehouse workers: They load and unload trucks, pallets, and other cargo.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers: They sort and package freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales reps are people who sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents: They are responsible for purchasing goods and services to support company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Ship clerks - They issue bills and process shipping orders.
-
Order fillers: They fill orders based off what has been ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others – There are many other types available in logistics. They include transport supervisors, cargo specialists and others.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is "the application statistical process control (SPC), techniques for continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department developed it at their Tokyo plant in Japan in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted Six Sigma in recent years because they believe that there are no perfect products and services. Six Sigma seeks to reduce variation between the mean production value. It is possible to measure the performance of your product against an average and find the percentage of time that it differs from the norm. If it is too large, it means that there are problems.
Understanding the nature of variability in your business is the first step to Six Sigma. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. It is important to identify whether the variations are random or systemic. Random variations occur when people make mistakes; systematic ones are caused by factors outside the process itself. You could consider random variations if some widgets fall off the assembly lines. It would be considered a systematic problem if every widget that you build falls apart at the same location each time.
After identifying the problem areas, you will need to devise solutions. It might mean changing the way you do business or redesigning it entirely. You should then test the changes again after they have been implemented. If they don't work, you will need to go back to the drawing boards and create a new plan.