
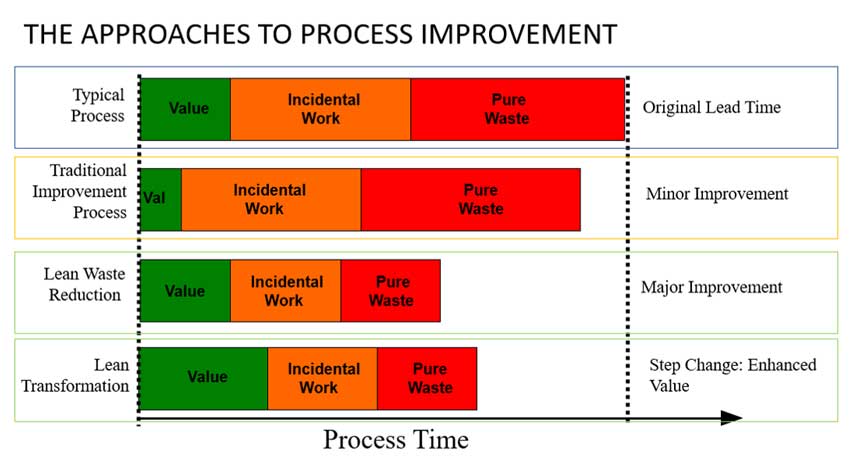
The Lean 5 principles stress the elimination of all waste, even those that don't add value to the product. Value stream mapping helps identify efficient and cost-effective activities. The key to eliminating waste is to separate value-added, (necessary), waste from non-value added (unnecessary). The simplest process can be made to use the most energy and time. This helps produce the highest quality products in the shortest amount of time, while keeping customers satisfied.
Value
You can improve the flow of manufacturing by eliminating waste using the Value of Lean 5 principles. The key to smooth production-to-shipping flow is identifying and eliminating those steps that don't add any value. You can also reduce the amount of inventory you have and make it easier to save time.
Value stream
Lean manufacturing uses the value stream to reduce waste. The process maps out every step in a process to identify and eliminate the necessary elements. The entire lifecycle of a product is included in the value stream. It includes its initial conception, use, and eventual disposal. This is the key to eliminating all waste. There are three types waste in a value stream.
Flow
The first of 5 lean principles, Flow, involves identifying customers' actual needs and evaluating them. This is an important step in the design process for new products and/or services. Customers do not always articulate their needs clearly. The second step is to define the value stream. This is the list of activities that will complete your project. This requires close collaboration from all project participants.
Pull
In a pull system, the process begins only when there is an order from a customer. A pizza restaurant wouldn't make extra pizzas unless they received a order from a customer. This would mean they would waste resources, time, and food.
Perfection
One of 5 principles of lean is the pursuit for perfection. This concept defines perfection as a state that is perfect, precise, consistent, and complete. However, achieving perfection is an elusive goal. The idea behind this concept is to promote continuous improvement. Organizations can achieve a higher performance level by doing this.

Collaborative efforts of all stakeholders
Stakeholder collaboration is a crucial element in lean project administration. It entails collaboration between project team members to solve problems and increase project value. In the planning stage, teams should identify problems and areas of improvement. The doing stage is more about data gathering and execution than it is about executing. For collaboration, the team must also take into consideration the organizational structure.
FAQ
What is the importance of automation in manufacturing?
Automation is essential for both manufacturers and service providers. Automation allows them to deliver services quicker and more efficiently. It helps them to lower costs by reducing human errors, and improving productivity.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The main difference between a production planner and a project manager is that a project manager is usually the person who plans and organizes the entire project, whereas a production planner is mainly involved in the planning stage of the project.
What skills is required for a production planner?
Being a production planner is not easy. You need to be organized and flexible. You must also be able to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
Statistics
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just In-Time Production Method
Just-in-time (JIT) is a method that is used to reduce costs and maximize efficiency in business processes. It's a way to ensure that you get the right resources at just the right time. This means that you only pay for what you actually use. The term was first coined by Frederick Taylor, who developed his theory while working as a foreman in the early 1900s. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
JIT teaches you to plan ahead and prepare everything so you don’t waste time. You should also look at the entire project from start to finish and make sure that you have sufficient resources available to deal with any problems that arise during the course of your project. If you expect problems to arise, you will be able to provide the necessary equipment and personnel to address them. This will prevent you from spending extra money on unnecessary things.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This type of JIT allows you to order the parts/materials required for your project on a regular basis. This will allow for you to track the material that you have left after using it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows you to predict how much you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT is the most widespread form. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. For instance, if you have a lot of orders coming in, you'll assign more people to handle them. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based: This is a similar approach to resource-based but you are not only concerned with how many people you have, but also how much each one costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each employee, you will focus on the time it takes to complete a project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: This is the latest form of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, you're focused on how much value you add to the market.
-
Stock-based: This stock-based method focuses on the actual quantity of products being made at any given time. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-in-time (JIT) planning: This is a combination of JIT and supply chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.