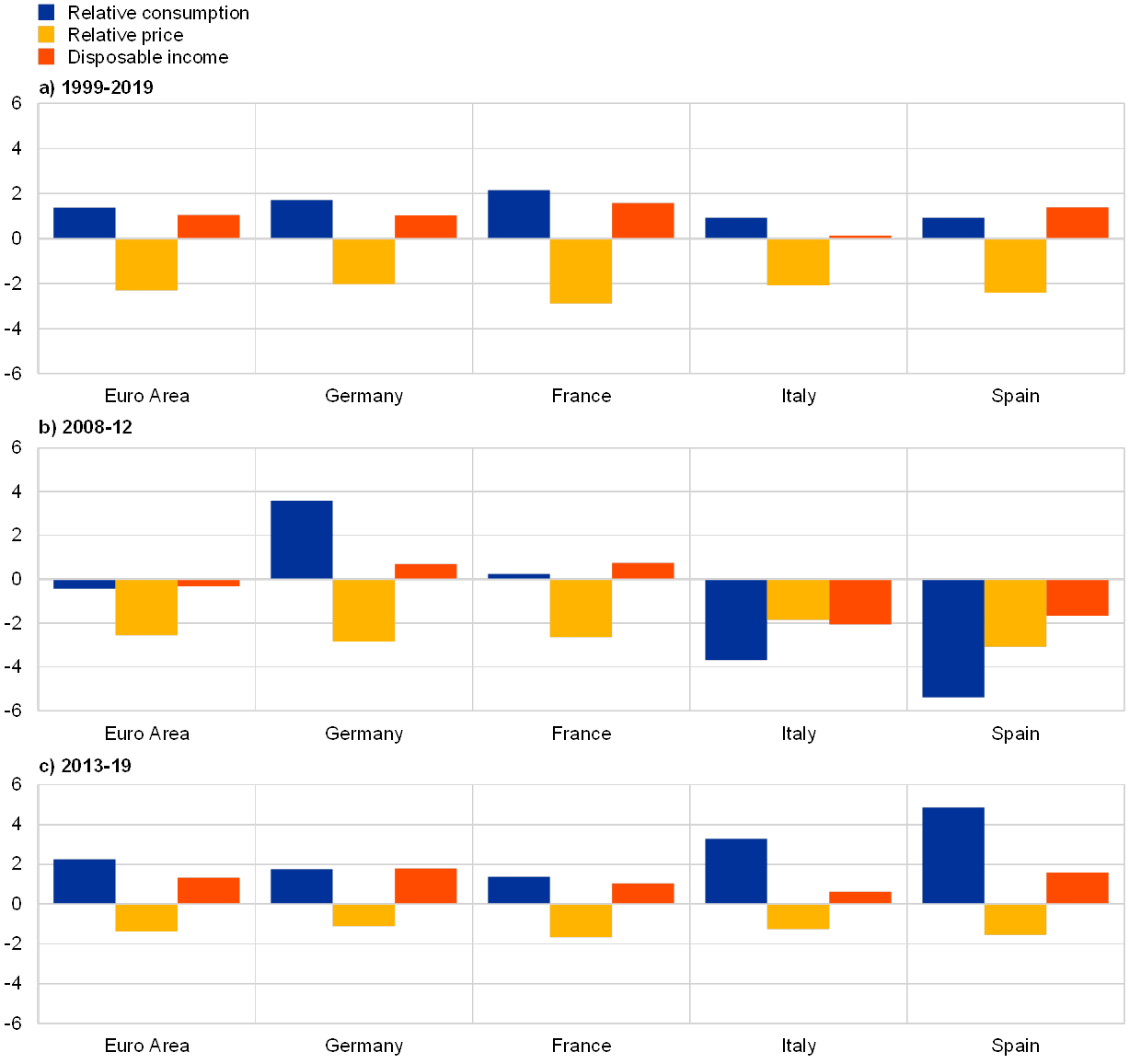
Across industries, supply chain disruptions have caused long-term productivity deficits and economic losses. The disruptions have been caused by companies' failure to manage risk effectively.
In the face of growing internationalization, the defence industry has been affected by this trend. There may be a shortage of certain technologies, such high-quality carbon-fiber and advanced semiconductors. This can lead both to increased dependence and oligopolistic behavior. Additionally, dual products are more likely to be used. These products could pose safety and reliability issues.
Globalization means that the security of crucial minerals is vital to the development and maintenance of modern industrial systems. Certain minerals can be found in economically poor countries, making them vulnerable to political instability. Under different circumstances, the global optimal allocation of critical mineral resources changes. China is a crucial node in a global critical minerals value chain. However the industry is highly dependent upon other nations. It is important that governments establish a global critical metal allocation network that includes multiple nations, instead of concentrating resources within a single nation.
Discussions have been held by the European Union (EU), regarding its defense technology and industrial base (DTIB). The European Commission established the European Defence Agency in order to provide a framework to develop a new European defense industry. This new approach will result in a variety of changes to the EU's defense industry. Certain technologies cannot be supplied by all non-EU companies. In the EU's defense sector, there will be both oligopoly as well as monopoly structures. In addition, it will become easier to buy certain raw materials from non-EU companies. This will open the door to a new type, called bundled volume.
A greater emphasis is being placed on developing a resilient and secure supply chain. There are many strategies to mitigate supply chain disruptions. One strategy is the implementation of a formal risk-management approach. Investing in a formal risk management approach can enable the supply chain to thrive, rather than just survive. It should include key stakeholders from both the internal and external world, such as suppliers, investors, and government. The supply chain should also be managed in accordance with global supply chain dynamics.
The security of the 99m/99m Tc supply chains is another important policy issue. The policy approach that was developed by the High-Level Group on Medical Radioisotopes, (HLG-MR), ensures long-term security in the supply of these radioisotopes. The policy approach was comprised of several elements. These included a review on the global 99m/99mtc supply chains, an analysis and a strategy approach.

HLG-MR identified two areas of vulnerability that must be addressed to increase the security of the 99 M/99m supply chain. These areas include monopolistic behaviour, foreign capital, and political conflicts. These factors could lead to significant price increases or risks. HLG-MR developed a policy approach that identified key steps that could be taken to address these weaknesses.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehouses are increasingly dependent on automation. E-commerce has increased the demand for quicker delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. Technology is essential for warehouses to be able to adapt quickly to changing needs. Automating warehouses is a great way to save money. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety increases
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies scale more easily
-
Increases efficiency of workers
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
This ensures that quality products are delivered promptly
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
It ensures compliance with regulations
What are the products of logistics?
Logistics refers to all activities that involve moving goods from A to B.
They cover all aspects of transportation, such as packing, loading, transporting and unloading.
Logisticians ensure that products reach the right destination at the right moment and under safe conditions. Logisticians help companies improve their supply chain efficiency by providing information about demand forecasts and stock levels, production schedules, as well as availability of raw materials.
They also keep track of shipments in transit, monitor quality standards, perform inventories and order replenishment, coordinate with suppliers and vendors, and provide support services for sales and marketing.
Is there anything we should know about Manufacturing Processes prior to learning about Logistics.
No. No. However, knowing about manufacturing processes will definitely give you a better understanding of how logistics works.
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), or production planning, is the process by which you determine what products are needed at any given time. Forecasting and identifying production capacity are two key elements to this process.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
What is the responsibility for a logistics manager
A logistics manager makes sure that all goods are delivered on-time and in good condition. This is accomplished by using the experience and knowledge gained from working with company products. He/she must also ensure sufficient stock to meet the demand.
Is it possible to automate certain parts of manufacturing
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The wheel was invented by the Egyptians thousands of years ago. To help us build assembly lines, we now have robots.
In fact, there are several applications of robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that make products
There are many other examples of how manufacturing could benefit from automation. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma: How to Use it in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined by "the application SPC (statistical process control) techniques to achieve continuous improvements." It was developed by Motorola's Quality Improvement Department at their plant in Tokyo, Japan, in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. This method has been adopted by many companies in recent years as they believe there are no perfect products or services. The main goal of Six Sigma is to reduce variation from the mean value of production. You can calculate the percentage of deviation from the norm by taking a sample of your product and comparing it to the average. If the deviation is excessive, it's likely that something needs to be fixed.
Understanding the nature of variability in your business is the first step to Six Sigma. Once you've understood that, you'll want to identify sources of variation. These variations can also be classified as random or systematic. Random variations happen when people make errors; systematic variations are caused externally. Random variations would include, for example, the failure of some widgets to fall from the assembly line. You might notice that your widgets always fall apart at the same place every time you put them together.
After identifying the problem areas, you will need to devise solutions. That solution might involve changing the way you do things or redesigning the process altogether. You should then test the changes again after they have been implemented. If they didn't work, then you'll need to go back to the drawing board and come up with another plan.