
Classic economics has three basic sectors. Manufacturing, services, and financial activities can be classified into these three categories. The characteristics and risks that businesses face are what determine how they are classified. Learn more about each one of the three sector groups below. Below is a brief overview about the types of businesses found in each sector. You can further dive into this information if you are interested. These categories do not have to be mutually exclusive.
Economic activity
Factors such as production, inputs, outputs are key to determining the economic activity of any nation or country. A region's ability to produce a particular product or service determines its economic activity. There are two types economic activity: primary or secondary. Primary economic activities produce goods and services that satisfy human needs. While secondary economic activities add value by combining raw materials into a better product, they are not as valuable. Manufacturing and processing are two examples of secondary activities.
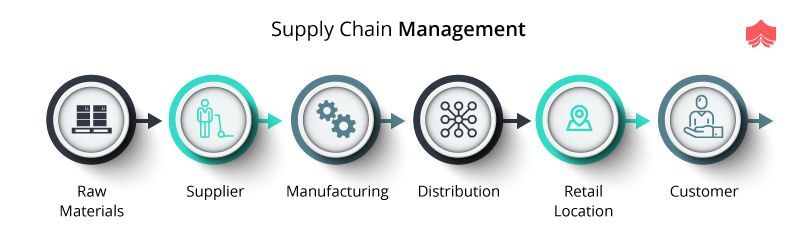
Classification
Business classification refers the process of dividing businesses in groups based their type of activities. There are two main categories: primary and secondary. Primary businesses are those who extract and exchange natural resource. The second kind of business converts raw materials and produces products for sale. There are many differences among these types of businesses. Here are some major differences between both types. You can use the information from this article to help you decide which type of business is best for your company.
Characteristics
Below is a discussion that explains the differences among the primary, secondary, tertiary and tertiary industries and how they impact the economy. First, let's define sectors. Sectors can be considered unique economic entities. They respond differently depending on different factors. These conditions may occur repeatedly, like business cycles. Or they could be unique events, like technological advancements. These characteristics can be used to identify the most lucrative sectors and to determine their relative importance in an economy.
Risques
Industry risk refers the variation in performance among industries and between companies. It can be measured using the variance in ROE and profitability. This may be influenced by the performance of stock market stocks, depending on the industry. A company that makes steel is high-risk because of the possibility for major earthquakes in the area. A study of such risks may help investors determine which sectors are more volatile.
Investments
Although many investors prefer to invest in companies, it is possible to invest in sectors. Sectors offer lower risks and can be found in mutual funds and exchange-traded funds. Sector investing is also becoming a popular investment strategy. This article will discuss how sector investing can help you find the right investments. For more information, please read on. And don't forget to check out our free resource section for more information.
FAQ
What are manufacturing and logistic?
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. As a broad term, manufacturing and logistics often refer to both the creation and delivery of products.
Can certain manufacturing steps be automated?
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. Nowadays, we use robots for assembly lines.
There are many uses of robotics today in manufacturing. They include:
-
Robots for assembly line
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
There are many other examples of how manufacturing could benefit from automation. For example, 3D printing allows us to make custom products without having to wait for weeks or months to get them manufactured.
How can we reduce manufacturing overproduction?
The key to reducing overproduction lies in developing better ways to manage inventory. This would reduce the amount of time spent on unnecessary activities such as purchasing, storing, and maintaining excess stock. This would allow us to use our resources for more productive tasks.
This can be done by using a Kanban system. A Kanbanboard is a visual tool that allows you to keep track of the work being done. Kanban systems are where work items travel through a series of states until reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority level.
For instance, when work moves from one stage to another, the current task is complete enough to be moved to the next stage. However, if a task is still at the beginning stages, it will remain so until it reaches the end of the process.
This keeps work moving and ensures no work is lost. Managers can view the Kanban board to see how much work they have done. This data allows them adjust their workflow based upon real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another option to control inventory levels. Lean manufacturing works to eliminate waste throughout every stage of the production chain. Any product that isn't adding value can be considered waste. The following are examples of common waste types:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Material surplus
These ideas can help manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce costs.
What type of jobs is there in logistics
There are many kinds of jobs available within logistics. These are some of the jobs available in logistics:
-
Warehouse workers – They load, unload and transport pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers: They sort and package freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators: They plan and manage logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service agents - They answer phone calls and respond to emails.
-
Shippers clerks - They process shipping order and issue bills.
-
Order fillers: They fill orders based off what has been ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors (QCI) - They inspect all incoming and departing products for potential defects.
-
Other - Logistics has many other job opportunities, including transportation supervisors, logistics specialists, and cargo specialists.
What are the responsibilities of a logistic manager?
Logistics managers make sure all goods are delivered on schedule and without damage. This is achieved by using their knowledge and experience with the products of the company. He/she should ensure that sufficient stock is available in order to meet customer demand.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. With the rise of ecommerce, there is a greater demand for faster delivery times as well as more efficient processes.
Warehouses must adapt quickly to meet changing customer needs. Technology investment is necessary to enable warehouses to respond quickly to changing demands. The benefits of automating warehouses are numerous. These are just a few reasons to invest in automation.
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety Boosts
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies to scale more easily
-
Increases efficiency of workers
-
Provides visibility into everything that happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reduces downtime and improves uptime
-
High quality products delivered on-time
-
Removing human error
-
This helps to ensure compliance with regulations
What is the job of a manufacturer manager?
A manufacturing manager must ensure that all manufacturing processes are efficient and effective. They should be aware of any issues within the company and respond accordingly.
They must also be able to communicate with sales and marketing departments.
They should also be aware of the latest trends in their industry and be able to use this information to help improve productivity and efficiency.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma and Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined by "the application SPC (statistical process control) techniques to achieve continuous improvements." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department created Six Sigma at their Tokyo plant, Japan in 1986. The basic idea behind Six Sigma is to improve quality by improving processes through standardization and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted this method in recent years. They believe there is no such thing a perfect product or service. Six Sigma seeks to reduce variation between the mean production value. You can calculate the percentage of deviation from the norm by taking a sample of your product and comparing it to the average. If there is a significant deviation from the norm, you will know that something needs to change.
Understanding how your business' variability is a key step towards Six Sigma implementation is the first. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. These variations can also be classified as random or systematic. Random variations are caused when people make mistakes. While systematic variations are caused outside of the process, they can occur. If you make widgets and some of them end up on the assembly line, then those are considered random variations. However, if you notice that every time you assemble a widget, it always falls apart at exactly the same place, then that would be a systematic problem.
After identifying the problem areas, you will need to devise solutions. The solution could involve changing how you do things, or redesigning your entire process. To verify that the changes have worked, you need to test them again. If they don't work, you will need to go back to the drawing boards and create a new plan.